What is FTTH?
Fiber-To-The-Home refers to the use of optical fiber to reach the living space of the end user. FTTH uses a series of passive devices and components such as optical fibers to realize a fully passive network from the operator’s central office to the end user’s living space, providing users with high-speed and stable telecommunications, broadcasting, and Internet services.
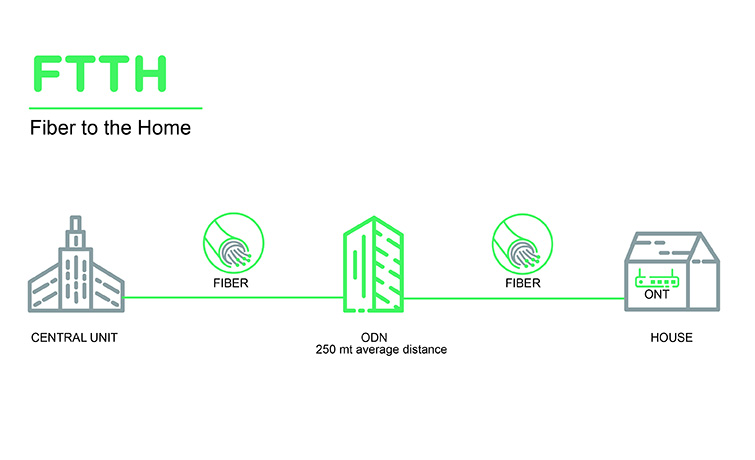
The defining feature of FTTH is that it connects fiber optics directly to residences. Fiber optics are used in most or all last-mile telecommunications. Fiber optics use optical signals to transmit data to achieve higher performance.

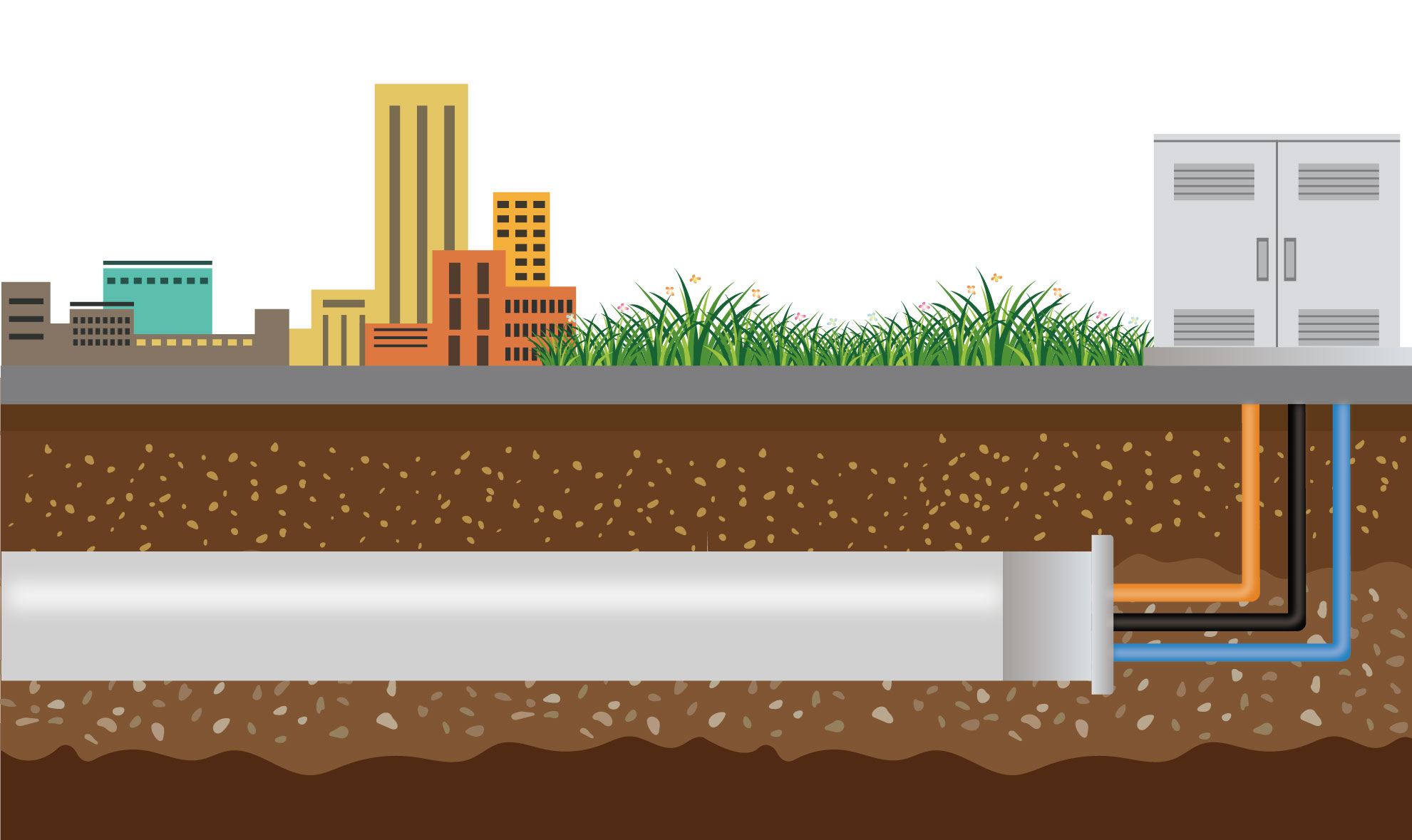
Pipeline Optic Cable
Pipeline optical cable is usually installed inside the pipeline and is physically protected by the pipeline to reduce the impact of the external environment on the optical cable. It usually has corrosion resistance to ensure long-term stable operation.
 View More
View More
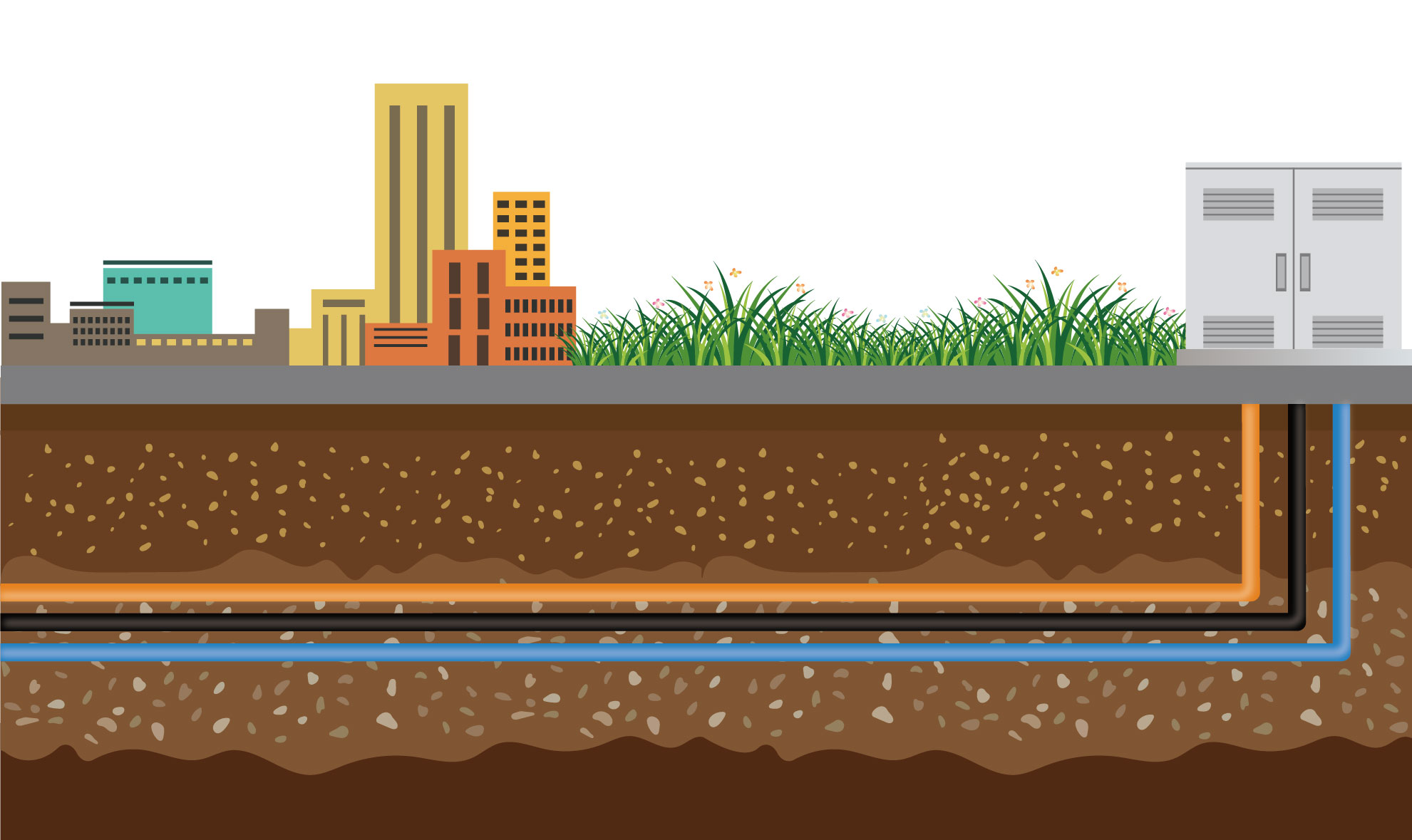
Direct Buried Optic Cable
Direct buried optical cable is a fiber optic cable directly buried underground to transmit data and communication signals. It usually has wear resistance and corrosion resistance, can resist the influence of the underground environment, and anti-interference, is less susceptible to electromagnetic interference, and provides more stable data transmission quality.
 View More
View More
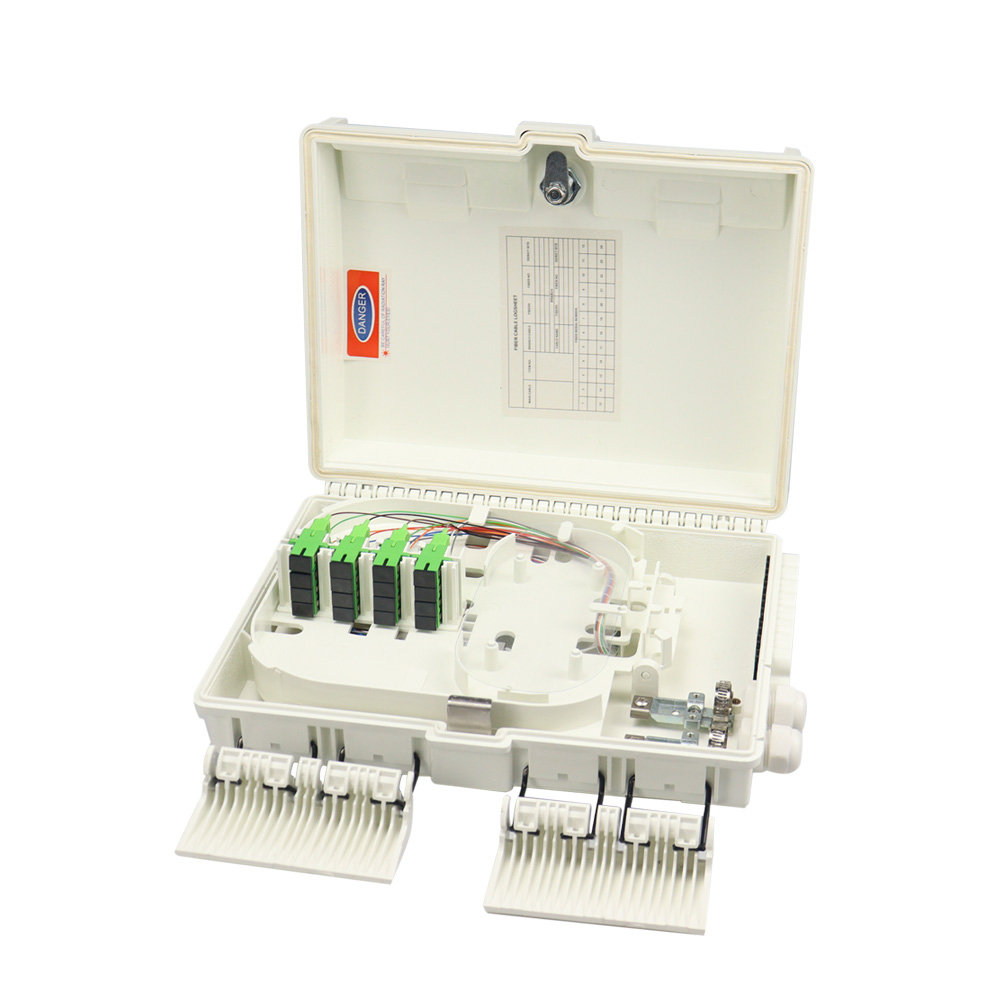
Fiber Distribution Box
A Fiber Distribution Box (FDB) is a type of enclosure used in fiber optic networks to manage and distribute optical fibers. These boxes provide a centralized location for terminating, splicing, and connecting fiber optic cables in indoor or outdoor environments.
 View More
View More
Air-Blown Micro Cable
Air Blown Micro Cable is a fiber optic cable designed to be installed using air-blowing techniques. Instead of traditional methods like pulling or pushing cables into conduits, air-blown micro cables use compressed air to install the fibers into micro ducts.
 View More
View More
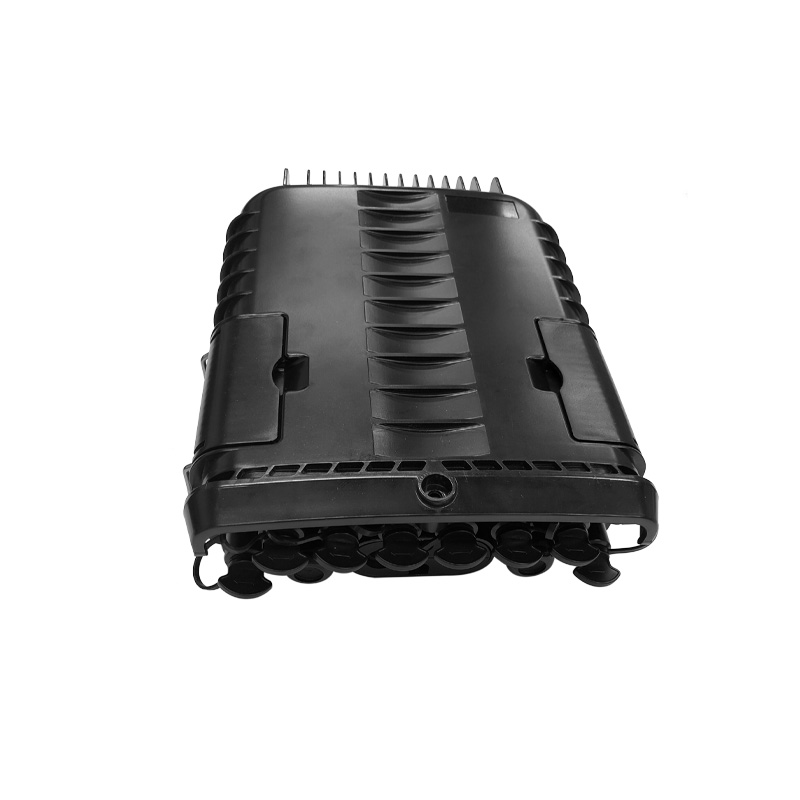
Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Fiber optic splice closures are devices used to join and protect optical fibers in outdoor environments. These closures provide protection for the fiber optic splices and connections from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and physical stress.
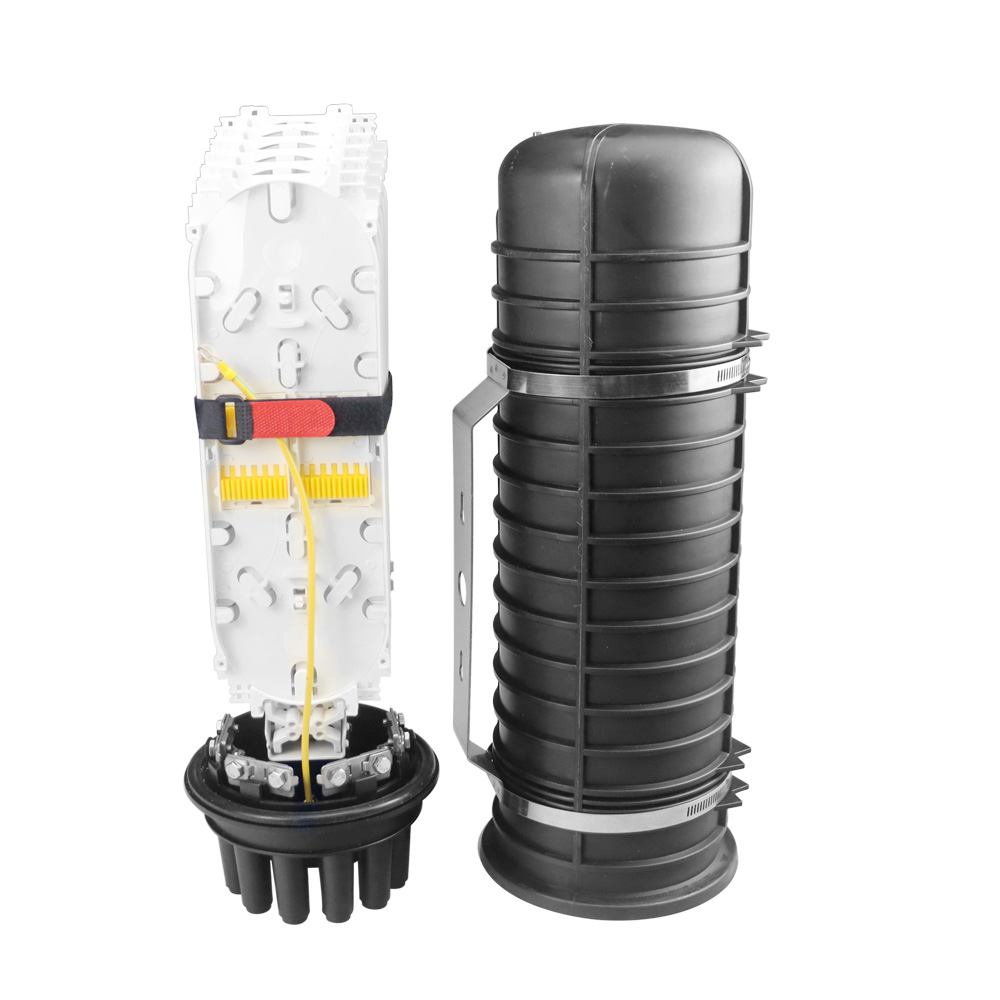 View More
View More
Fiber Optic Splice Closures
Fiber optic splice closures are devices used to join and protect optical fibers in outdoor environments. These closures provide protection for the fiber optic splices and connections from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and physical stress.
FTTx Drop Cable
A Fiber Drop Cable is a type of fiber optic cable specifically designed for connecting the distribution network to individual end-users in applications like Fiber to the Home (FTTH) or Fiber to the Building (FTTB). These cables are used to extend the fiber optic connection from the distribution point to the subscriber's premises.
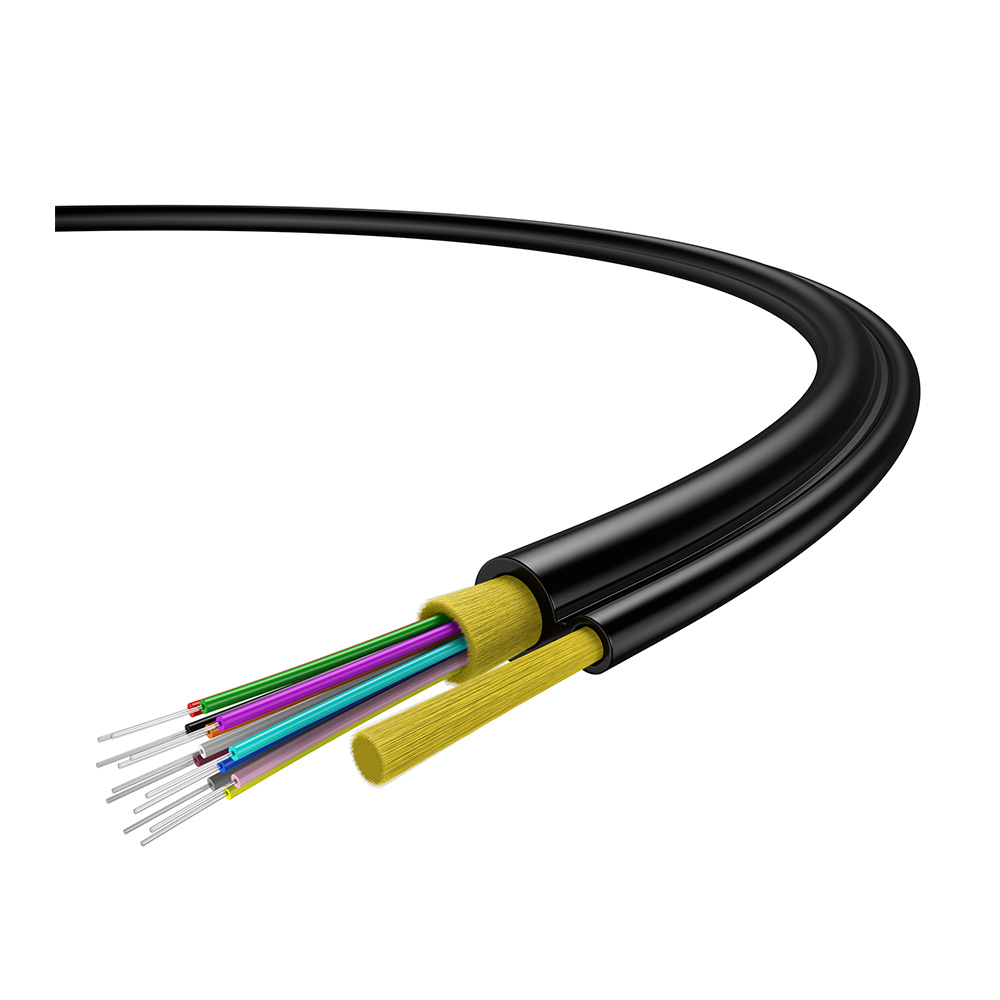 View More
View More
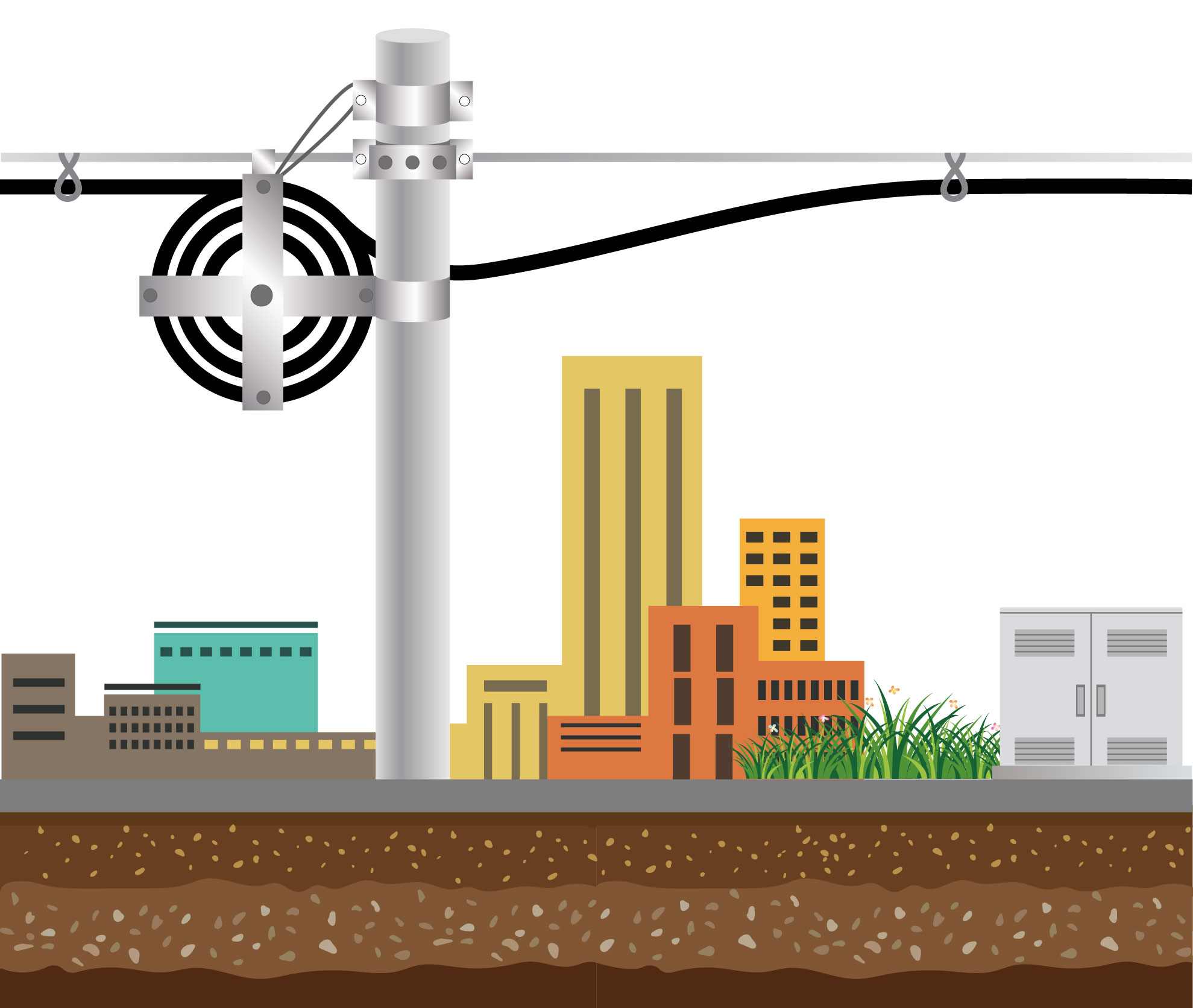
Aerial Fiber Optic Cable
Aerial fiber optic cable is a type of fiber optic cable used to transmit data and communication signals, usually mounted on utility poles, viaducts, or other support structures. Overhead fiber optic cable usually consists of multiple optical fibers, each of which can transmit a large amount of data. This type of fiber optic cable connects communication facilities in different locations through the air and is a widely used communication infrastructure in both urban and rural areas.
 View More
View More
Fiber Rosette Box
A Fiber Rosette Box is a type of enclosure used in fiber optic networks for indoor fiber optic cable termination and management. These boxes are typically installed in residential or small business settings to provide a neat and organized solution for terminating and distributing fiber optic cables within a building.
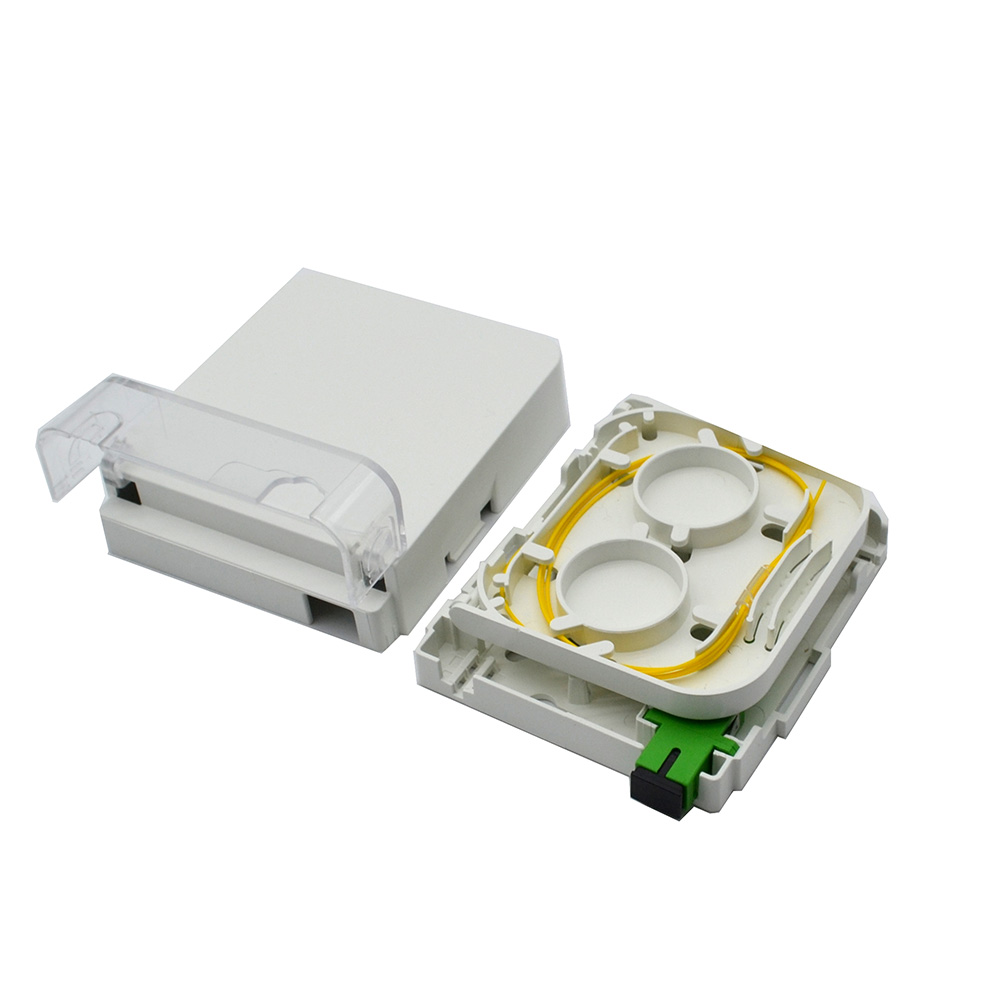 View More
View More
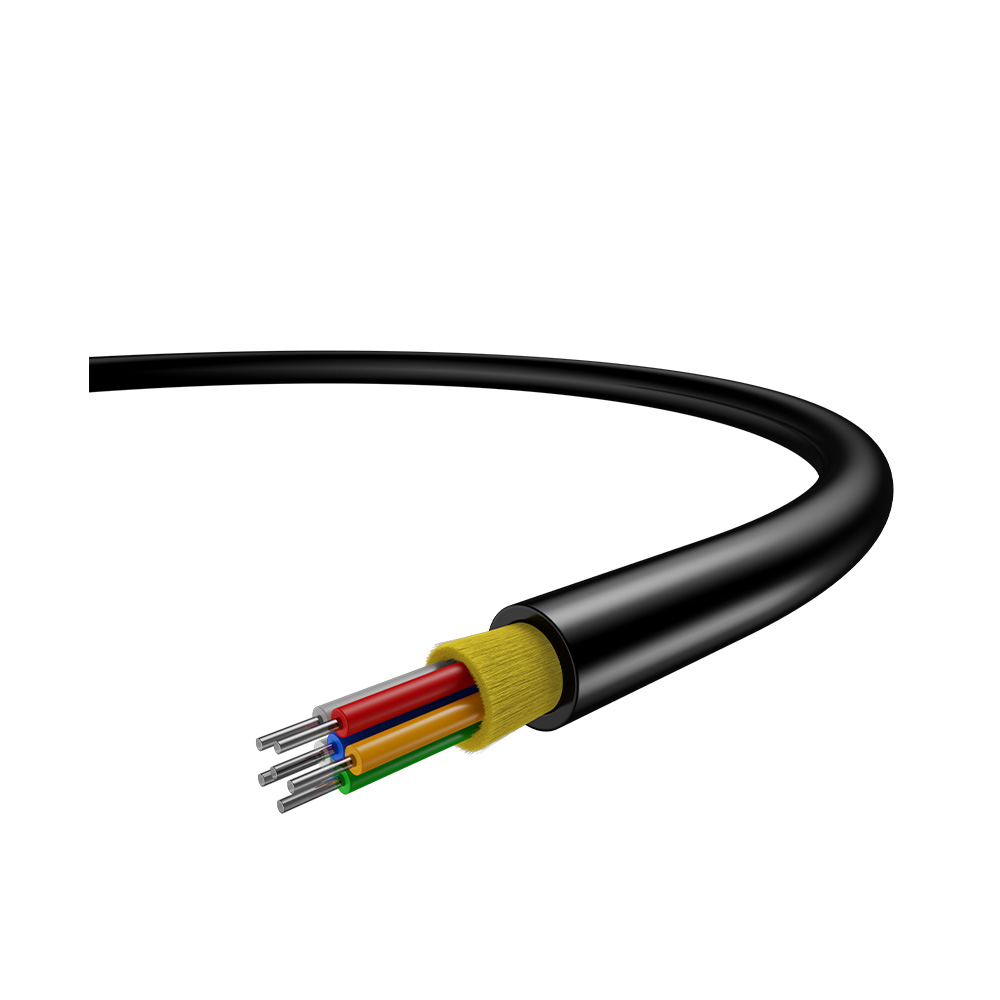
Indoor Optic Cable
Indoor fiber optic cables are designed for use inside buildings to establish connections between network equipment, such as data centers, telecommunication rooms, and other indoor locations where fiber optic connectivity is required. These cables are optimized for indoor environments and are not designed to withstand the harsh conditions typically found in outdoor installations.
 View More
View More





